Stepper motors are popular for their ability to stop accurately as well as their ease of use. Both the amount of rotation and the speed are controlled easily with the same digital square wave pulse signal. Unlike servo motors, stepper motors do not need an encoder to operate. Example applications of stepper motors are CNC machines, index tables, robotics, scanners, and more recently, 3D printers.
There are a variety of stepper motors available in the market. The most popular type of motor is the hybrid type, which combines the permanent magnet from the permanent magnet type, and the tooth construction from the variable reluctance type. With the hybrid type, there are 2-phase, 5-phase, and high resolution designs. Motors can also be pre-assembled with additional options for different purposes. For example, there are motors with an electromagnetic brake, encoder, or gearhead.
| Application: Performing quick indexing operations over short distances |
| Recommended: High torque 2-phase stepper motors |
 are the most common type used, and they are everywhere from ATM machines to slot machines. These motors offer high torque at low speeds and are ideal for general position control applications. NEMA frame sizes range from 8~34 (20 mm [0.79"] to 90 mm [3.35"]), and torque ranges from approximately 2.8 oz-in to 22,255 oz-in on different stack lengths. 4, 6, or 8 lead wires are offered for bipolar and unipolar drivers.
are the most common type used, and they are everywhere from ATM machines to slot machines. These motors offer high torque at low speeds and are ideal for general position control applications. NEMA frame sizes range from 8~34 (20 mm [0.79"] to 90 mm [3.35"]), and torque ranges from approximately 2.8 oz-in to 22,255 oz-in on different stack lengths. 4, 6, or 8 lead wires are offered for bipolar and unipolar drivers.
In linear motion applications, they are often combined with external mechanisms, such as pulleys and belts for indexing conveyors, or ball screws for  . Although they are traditionally used for low speed applications, more designs are adopting bipolar-parallel winding type motors for better high speed performance.
. Although they are traditionally used for low speed applications, more designs are adopting bipolar-parallel winding type motors for better high speed performance.
|
PKP Series 2-Phase Stepper Motor |

|
 |
| Application: Achieving a high-speed reciprocating motion with less vibration |
| Recommended: High torque 5-phase stepper motors |
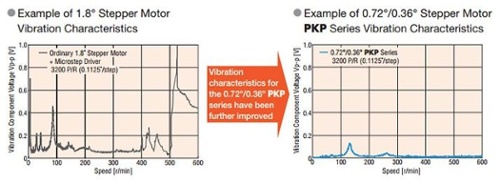
 with an improved high speed winding design are suitable for applications that require fast reciprocating motions. Vibration is considerably lower than 2-phae stepper motors even without microstepping. Instead of a typical 1.8° per step resolution, these motors have a step resolution of 0.72°. These motors are ideal for applications that are sensitive to noise or vibration, such as laboratory instruments.
with an improved high speed winding design are suitable for applications that require fast reciprocating motions. Vibration is considerably lower than 2-phae stepper motors even without microstepping. Instead of a typical 1.8° per step resolution, these motors have a step resolution of 0.72°. These motors are ideal for applications that are sensitive to noise or vibration, such as laboratory instruments.
|
PKP Series 5-Phase Stepper Motor |
 |
 |
Since the basic step angle is small at 0.72° (0.36° for high-resolution type), the vibration and noise are considerably lower than 2-phase stepper motors with a basic step angle of 1.8°.
| Application: Performing indexing operations of large inertial loads |
| Recommended: Geared stepper motors |
A  can rotate a larger inertial load, such as a robotic arm, due to its ability to generate much higher torque than a round-shaft, ungeared motor, and to reduce the inertia ratio between the load and the motor.
can rotate a larger inertial load, such as a robotic arm, due to its ability to generate much higher torque than a round-shaft, ungeared motor, and to reduce the inertia ratio between the load and the motor.
 |
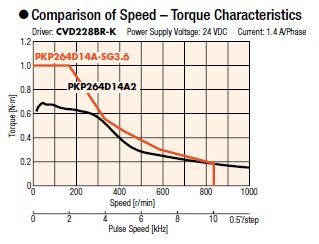 |
If the motor is not sized properly, large inertial loads can exceed the motor's recommended inertia ratio and cause missed steps due to overshooting or undershooting. Using a geared type stepper motor also increases the motor's ability to handle axial and radial loads.
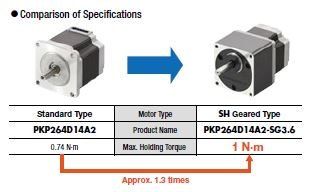
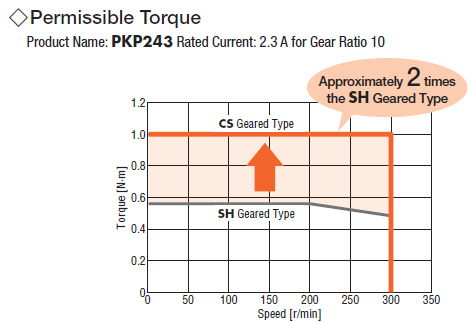
The new CS type centered shaft spur geared stepper motors offer improved torque, axial load, radial load, and backlash characteristics than the traditional SH type offset shaft spur geared stepper motors. For users who prefer a centered shaft, the CS centered provides a low cost alternative to planetary gearheads. For users who prefer more torque or accuracy, planetary and harmonic geared motors are also available.
|
PKP Series CS Geared Type Stepper Motor |
 |
For space-saving machine designs, a geared type motor can drive heavier loads while keeping the motor frame size compact.
| Application: Performing indexing operations with higher stop accuracy |
| Recommended: High resolution type 2-phase stepper motors |
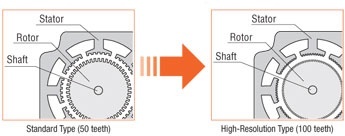
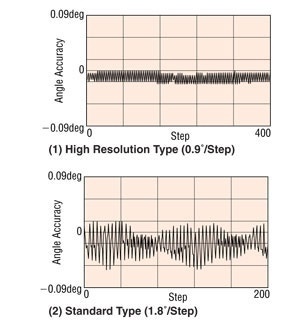
A  has 100 rotor teeth instead of 50 rotor teeth. The increase in rotor teeth doubles the basic step resolution of standard motors from 200 to 400 steps per revolution and offers better stop accuracy (2 arc min or 0.034° instead of 3 arc min or 0.05°).
has 100 rotor teeth instead of 50 rotor teeth. The increase in rotor teeth doubles the basic step resolution of standard motors from 200 to 400 steps per revolution and offers better stop accuracy (2 arc min or 0.034° instead of 3 arc min or 0.05°).
Similar to 5-phase stepper motors, high resolution type stepper motors can "half-step" without a microstepping driver, which can lower cost for certain applications.
|
PKP Series High Resolution Type Stepper Motor
|
 |
| Application: Performing vertical positioning operation with power-off braking |
| Recommended: Electromagnetic brake type stepper motors |
An  is a stepper motor with a built-in power-off-activated electromagnetic brake, which uses electromagnets and disc friction to hold the motor shaft in place. When power is removed or accidentally cut off, the electromagnetic brake can be used to hold a load in position to prevent it from dropping or moving, such as in a rack and pinion lift. With an electromagnetic brake, the motor current can also be turned off at standstill to suppress heat or lower power consumption.
is a stepper motor with a built-in power-off-activated electromagnetic brake, which uses electromagnets and disc friction to hold the motor shaft in place. When power is removed or accidentally cut off, the electromagnetic brake can be used to hold a load in position to prevent it from dropping or moving, such as in a rack and pinion lift. With an electromagnetic brake, the motor current can also be turned off at standstill to suppress heat or lower power consumption.
The electromagnetic brake is assembled at the rear of the motor, which increases the motor length.
|
PKP Series Electromagnetic Brake Type Stepper Motor |
 |
| Application: Performing closed-loop positioning operation |
| Recommended: Encoder type stepper motors |
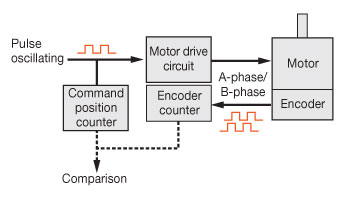
An  offers a pre-assembled encoder that provides a pulse signal for a host controller to track its actual position. Oriental Motor offers both our own compact reflective encoder or an optical encoder from US Digital. These motors are used for applications where position tracking is critical, such as in surgical robots. For 2-phase stepper motors, encoders are offered at either 200 PPR or 400 PPR to match the motor's basic step resolution. 500 PPR or 1,000 PPR are offered for 5-phase stepper motors. Voltage (TTL) and line driver output types are available with 3 channel output (A-phase, B-phase, and Z-phase).
offers a pre-assembled encoder that provides a pulse signal for a host controller to track its actual position. Oriental Motor offers both our own compact reflective encoder or an optical encoder from US Digital. These motors are used for applications where position tracking is critical, such as in surgical robots. For 2-phase stepper motors, encoders are offered at either 200 PPR or 400 PPR to match the motor's basic step resolution. 500 PPR or 1,000 PPR are offered for 5-phase stepper motors. Voltage (TTL) and line driver output types are available with 3 channel output (A-phase, B-phase, and Z-phase).
|
PKP Series Encoder Type Stepper Motor |
 |
| Application: Positioning within a small space |
| Recommended: Flat type stepper motors |
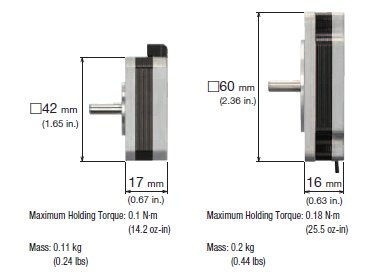
A  is a thin type of motor designed to fit into tight spaces. For applications such as index tables, small conveyors, or even robotics, flat type stepper motors can help minimize footprint. A 42 mm frame size and a 60 mm frame size (including a harmonic gear type) are available.
is a thin type of motor designed to fit into tight spaces. For applications such as index tables, small conveyors, or even robotics, flat type stepper motors can help minimize footprint. A 42 mm frame size and a 60 mm frame size (including a harmonic gear type) are available.
Thanks for reading this post.
Request a technical seminar for your team!
Subscribe at the top of the page for more tips.