As efficiency becomes increasingly important, another type of gear is being adopted for right-angle gearheads over the common worm gears.
Historically, worm gears have been known as the most common type of gears used in a right-angle gearhead. Their low cost and robust construction have been sufficient for general-purpose applications. However, they are inefficient at slower speeds (higher reduction ratios), generate a lot of heat, take up a lot of space, and require maintenance. As efficiency standards became increasingly important globally, another type of gear is being adopted for right-angle gearheads.
Typically used in automotive applications, hypoid gears have been integrated into right-angle gear motors to eliminate the problems caused by worm gears as well as to improve the performance of right-angle gear motors. The initial cost of hypoid gear motors may be higher than that of worm gear motors due to machining, heat treatment, and special grinding techniques, but long-term benefits can outweigh the initial cost for many applications.
Why Hypoid Gear Motors are Better Than Worm Gear Motors
In a worm gear set, there are two components: the input worm and the output worm gear. The input worm is a screw-like gear that rotates perpendicular to its corresponding output worm gear. In a worm gearhead with a 5:1 ratio, the input worm will complete 5 revolutions while the output worm gear will complete only one. However, torque is not multiplied by a factor of 5 since a lot of torque is lost through sliding friction.
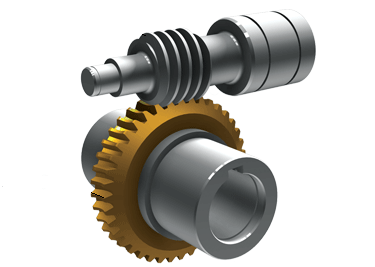
Source: https://www.motioncontroltips.com/worm-gears-what-are-they-and-where-are-they-used/
In comparison, the hypoid gear set consists of an input hypoid gear and an output hypoid bevel gear. Although the hypoid gear set is a hybrid of bevel and worm gear technologies, the gear efficiency is much higher even in high reduction ratios. The key is that the hypoid tooth pattern minimizes sliding friction between the gear teeth to allow more torque transfer from motor shaft to load shaft.
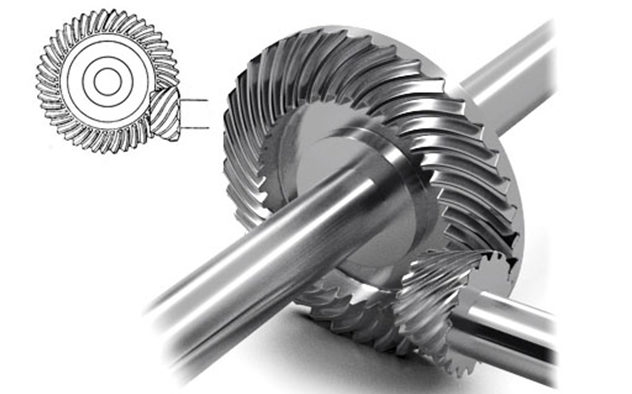
Source: https://www.motioncontroltips.com/hypoid-gearboxes-what-are-they-and-where-are-they-used/
In this post, we will summarize the performance differences between hypoid and worm gears from the white paper.
- Better gear efficiency
- Higher Torque, Thrust Load, and Overhung Load
- Less heat generation
- Smaller footprint
- Lower Power Consumption
✅Better Gear Efficiency
One of the biggest issues with worm gears is their low efficiency for torque transfer. Typically, worm gear efficiency can vary from 40% to 85% for ratios of 60:1 to 10:1 respectively. They also require a "break-in" period in order to run at peak efficiency. Hypoid gear efficiency is up at 95% to 99% and do not require a break-in period.
Due to increasing importance in reducing power consumption, efficiency is now one of the most important factors to consider when choosing a gear motor. Since motors already have a long life, choosing an efficient gearhead to go with the motor makes a lot of sense in reducing maintenance costs.
✅Higher Torque, Thrust Load, and Overhung Load
Due to higher gear efficiency and more space for bigger gears and bearings, a right-angle hypoid gear motor can generate up to 3.5x higher rated torque than another gear motor. The thrust load and overhung load are also higher.
 |
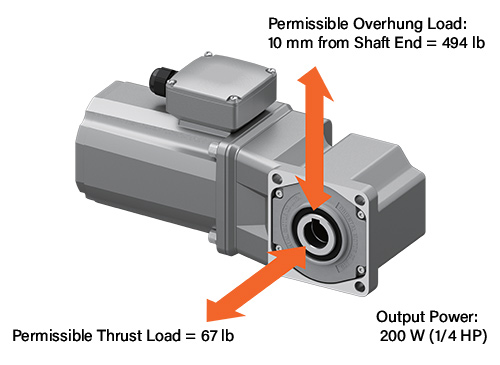 |
✅Less Heat Generation
A higher efficiency gearhead will waste less energy. Friction is wasted energy that takes the form of heat. Since worm gears produce more sliding friction than hypoid gears, they run hotter, which reduces the service life of these drivers by putting extra thermal stress on the lubrication, bearings, seals, and gears.
Since hypoid gears run cooler due to minimized sliding friction, there is little to do to keep them running at peak performance. There is no need to replace lubricants because the grease is meant to last the lifetime of the gear motor. This can help eliminate downtime and increase productivity. In addition, cooling fins, breather holes and other peripherals used for cooling is eliminated, contributing to lower operating costs.
When we run a hypoid gearbox and a worm gearbox with the same motor side by side, we found that when the temperatures leveled off, there is a significant difference of 26.4°F.
✅Smaller Footprint
Due to the way the axes of the gears intersect, the hypoid gear set requires a smaller footprint than worm gear sets. This helps in applications where space is a constraint. Another name for hypoid gears is screw bevel gears.
Another benefit of hypoid gear motors is that they are symmetrical axially from the motor shaft to the load shaft. Worm gear motors are asymmetrical and result in machines that are not as aesthetically pleasing, and mounting options are limited.

Source: gearmotors.org
Final Thoughts
The higher efficiency and design from hypoid gears presents many advantages over worm gears from higher load capacity, lower operating temperatures, smaller footprint, higher reliability, longer life, and lower power consumption. Using hypoid gears with high efficiency motors, such as high-efficiency AC motors or brushless DC motors, can improve efficiency even more.
This ultimately leads to lowering operating costs in the long run, and the ability to use smaller motors and design smaller machines. Although upfront costs can be higher for hypoid gears, these advantages should offer something to consider when selecting motors for your next machine design.
Oriental Motor offers right-angle hypoid gearhead options for three-phase AC induction motors from the K2S High-Efficiency Series and brushless DC motors from the BMU Series (includes driver with simple control) and BLE2 Series (includes driver with advanced control).
 |
|
 |
 |
|
TIP: Select a motor size by HP or watts, then use the filter options on the left side, and filter Shaft/Gear Type for "Right-Angle". Example:
|
Interested in receiving new articles in your inbox? Please subscribe at the top of this page.