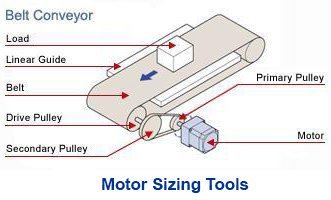
In today's fast-paced industrial landscape, the role of conveyors has become more crucial than ever. These systems efficiently move materials, products, and goods for numerous industries, from labeling and packaging to warehousing and distribution. While many types of motors can be used in conveyors, this article highlights a few reasons why brushless motors should be a primary choice for conveyor applications.
|
This article covers: |
Types of Motors Used for Conveyors
There are several types of motors that are typically used by conveyors; depending on the type of conveyor.
|
For fixed-speed conveyors where size isn't an issue, AC induction motors work well for their cost-effectiveness and ease of use, but gearheads are often necessary to lower the speed. Brush and brushless motors offer smaller footprint and can offer lower speeds without gearheads. |
|
| For variable-speed conveyors where multiple speeds are necessary, VFD-driven AC induction motors are common. In comparison, brushless motors can add speed regulation, extend the speed range, and help minimize footprint, and servo motors can provide even higher torque and speeds. |
|
| For indexing conveyors where repeatable stops and holding torque are required, stepper motors are generally chosen for their high stop accuracy. However, closed-loop stepper motors or servo motors can be considered when heat generation and limited duty cycles cause issues. |
|
Generally, brushless motors can be used for all types of conveyors that require high speed stability, high efficiency, and smaller footprint. They can even be used in start/stop conveyors if stop accuracy or holding torque aren't critical. Furthermore, they offer several advantages that make them ideal for many types of conveyors.
The Case for Brushless Motors
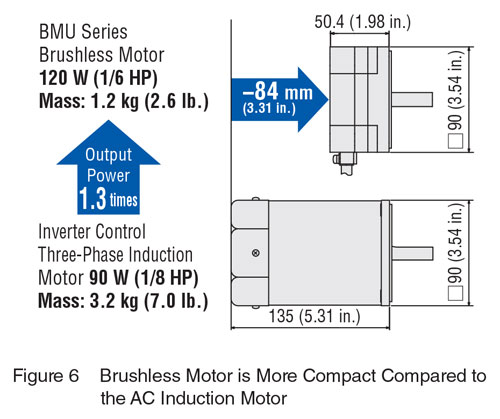
A brushless motor is generally smaller and lighter than other types of motors used in variable speed applications due to its design. For example, a brushless motor is smaller than a brushed motor due to the absence of brushes, and a brushless motor is shorter than a servo motor since it typically uses hall-effect sensor feedback instead of encoder feedback. However, these advantages are amplified when a brushless motor is compared to an AC induction motor, which is the most common type of motor used in conveyor applications.
A brushless motor can be made smaller than an AC induction motor because it is more efficient, runs cooler, and uses permanent magnets. By using permanent magnets in its rotor and an electromagnet stator to generate rotation, brushless motors do not have the same losses that occur during electromagnetic induction for AC motors.
Brushless Motors vs Other Speed Control Systems
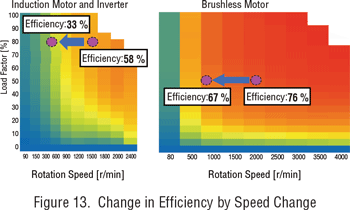
When compared to VFD-driven AC induction motors, brushless motors feature a smaller footprint, offer built-in closed-loop feedback and outputs constant torque. A brushless motor driver constantly monitors and adjusts the motor speed and torque according to the feedback from the motor, ensuring consistent performance even with load fluctuations; while the speed of an bigger, less efficient AC motor can be inconsistent due to open-loop operation and load fluctuations.
When compared to brushed DC motors, brushless motors are more expensive since they require closed-loop feedback and a dedicated driver to commutate the windings. A brushed motor uses brushes and a commutator, so no driver is required for commutation other than a variable voltage to control its speed. A brushless motor is also more efficient by design, draws less power, and is smaller in size. Brushless motors also do not have the regular brush and commutator maintenance that is necessary for brushed motors, which is a major advantage.
When compared to servo motors, brushless motors present a simpler solution in cases where servo motors can be oversized or overspec'ed. Brushless motors are actually very similar in design and operation to servo motors but uses lower resolution on the feedback and thus simpler control method and drive circuitry. Brushless motors can help keep costs low for conveyor applications that do not need the highest speeds, best top accuracy, or the peak torque offered by servo motor systems.
When compared to stepper motors, brushless motors are actually structurally similar except that it uses a radially magnetized rotor instead of an axially magnetized rotor. It also operates like one with power and phase excitation provided by a dedicated driver, but the similarities stop there. The lower number of poles and lack of holding torque are the main reasons why brushless motors do not offer the same stop accuracy as stepper motors. Therefore, stepper motors are recommended for positioning applications with a limited duty cycle, such as in indexing conveyors, and brushless motors, designed to run continuously, are a better match for continuous running variable-speed conveyors.
The table below summarizes the differences between AC motors, brushless motors, and servo motors.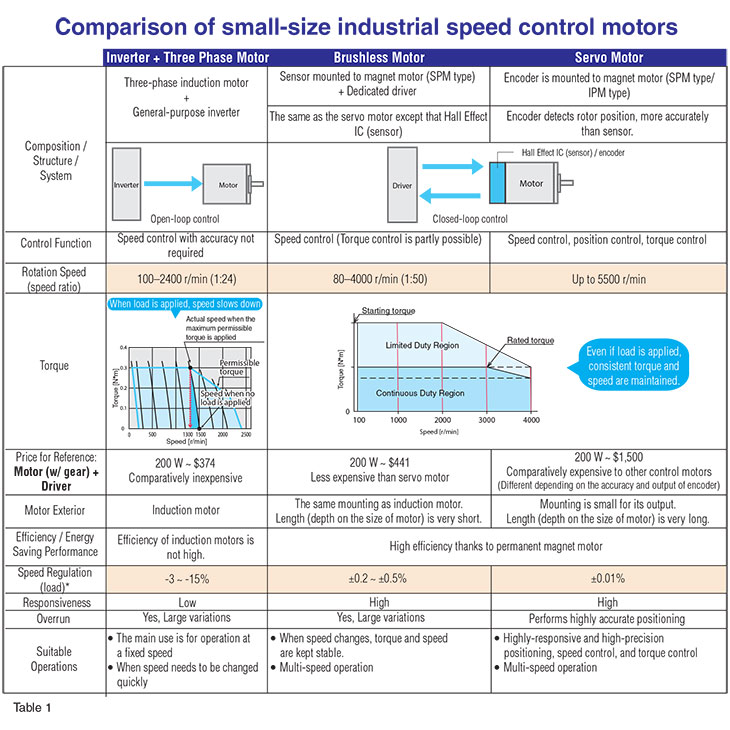 Additional speed control comparison information is available.
Additional speed control comparison information is available.
Here's a video that compares the power consumption and CO2 emissions of a 6 W AC induction motor vs a 30 W brushless motors on a conveyor. The difference is pretty clear.
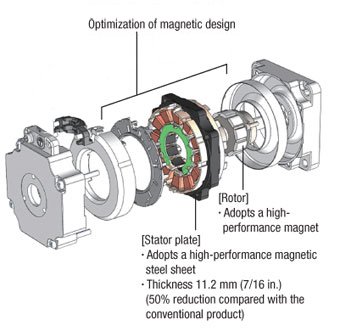
To further reduce its size, Oriental Motor's newest brushless motors combine an optimized magnetic design with high-performance magnetic steel sheets and permanent magnets. Closed-loop speed regulation for Oriental Motor's brushless motors is rated at +/-0.2% for motors with hall-effect sensors and up to +/-0.05% for motors with encoders. With a small overrun that ranges from approximately +/-0.1 to +/-0.4 revolutions according to the RPM and load inertia, brushless motors can also run some indexing conveyors. However, start/stop frequency and accuracy must be tested.
| Long-Life Type | Watertight | JB Gear Type | JV Gear Type | Right-Angle | Flat Hollow Shaft |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
With a wide lineup between 30 W and 400 W and different AC-input driver options, oversizing can be avoided with no sacrifice to performance. A variety of gear options are provided for even the smallest frame sizes, so even the smallest requirements can be sized properly. One major difference between Oriental Motor's brushless motors and other brushless motors is that we offer several different frame sizes for different wattages; while other manufacturers tend to keep the same frame size and increase the length of the motor.
Recommended Product Series by Conveyor Type
In this section, we highlight two types of conveyors that our AC-input brushless motor systems are typically used for: single-axis, modular, low-profile conveyors and packaging /labeling conveyors.
For single-axis modular low-profile conveyors with basic speed control requirements, a BMU Series brushless motor and dedicated variable speed driver are recommended.
| Single-Axis Modular Low-Profile Conveyors | For simple control, use: BMU Series |
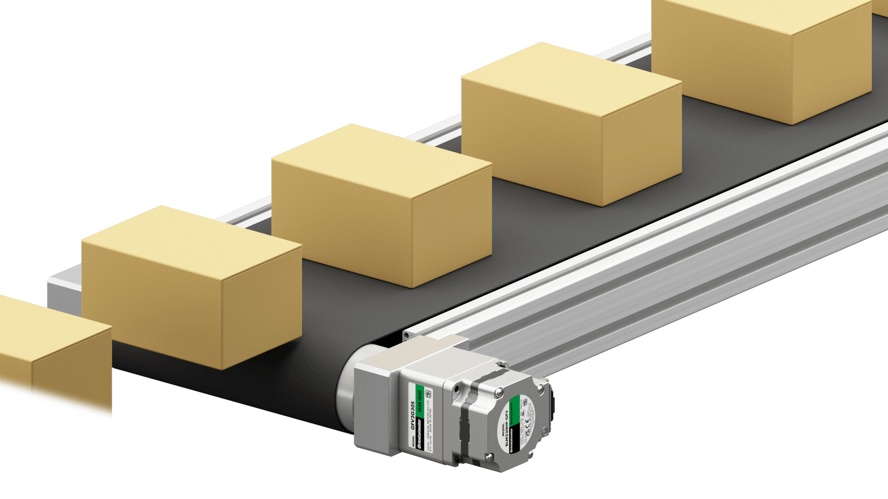
The simplicity of the BMU Series and ease-of-use of the front digital panel as well as easy connection makes it perfect for quick installation on single-axis, modular conveyors. The small size of the motor and driver helps reduce the footprint of the conveyor. The dedicated driver comes with built-in functions such as load factor and speed limits.
For conveyors with advanced requirements, such as for packaging and labeling, a BLE2 Series brushless motor and dedicated variable speed driver are recommended.
| Packaging and Labeling Conveyors | For advanced control, use: BLE2 Series |

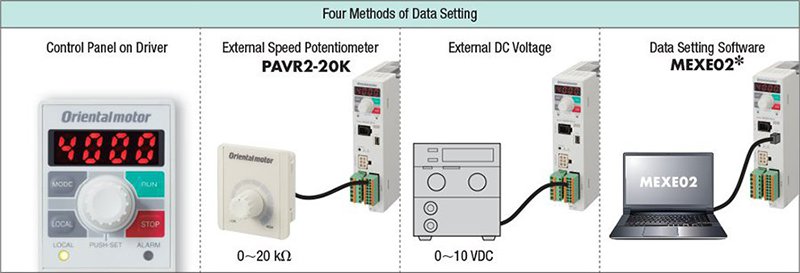
Up to 16 speeds can be set via the control panel, external potentiometer, external analog voltage, or MEXE02 data setting software. To run a grip conveyor that has two motors running two belts on each side of the product being transferred, an HMI can output an analog voltage to control 2 drives at the same time as well as output commands to each driver via I/O. The driver comes with functions such as load factor, torque-limiting, and speed teaching.
Summary
A brushless motor's high efficiency, small footprint, and tight speed regulation meet the design requirements of compact variable-speed conveyors. While a brushless motor presents many advantages over a VFD-driven AC motor, it can also replace brushed DC motors and even servo motors in certain applications.
While brushless motor design is similar among many manufacturers, Oriental Motor's brushless motors are offered in many frame sizes instead of longer stack lengths. Dedicated drivers guarantee motor performance and add enhanced capabilities such as speed teaching and torque limiting.
Make oversizing a thing of the past. Contact our team for a motor sizing consultation today to find the perfectly sized brushless motor and driver for your conveyors.
We know how engineers like charts. Here's a comparison of our two popular AC-input brushless motor systems featuring our most efficient brushless motor design. Feel free to reach out to our team for additional motor options tailored to meet other specific application requirements, like battery-compatibility or multi-axis network control.
| Series | BMU Series | BLE2 Series | |
 |
 |
||
| Equipment |
|
|
|
| Ideal Application Example | Single-axis drive | Side-by-side conveyor | |
| Wattages | 30 W (1/25 HP) , 60 W (1/12 HP), 120 W (1/6 HP), 200 W (1/4 HP), 300 W (2/5 HP), 400 W (1/2 HP) |
||
| Gear Types | Parallel, right-angle, hollow-shaft | Parallel, right-angle, hollow-shaft | |
| Key Features |
|
||
| Functions |
|
|
|
Want to learn how to size a motor for your conveyor? Here's an article about sizing motors for conveyors.