For machine designers who typically specify 3-phase AC induction motors and VFDs to meet variable speed requirements, brushless DC (BLDC) motors can be a cheat code to designing smaller, lighter, and more efficient machines. This article compares our 750 W (1 HP) Brushless DC Motor to an equivalent AC motor in efficiency, size/weight, and performance.
Topics covered:
- Introduction
- Motor Efficiency Comparison
- Size & Weight Comparison
- Speed Torque Performance Comparison
- Summary
Introduction
| The 750 W (1 HP) Brushless DC (BLDC) Motor is designed to be compact yet powerful. With tested compatibility with a variety of popular VFDs, it can easily replace much larger AC induction motors in machine designs that aim to reduce footprint while improving efficiency and lowering power consumption at the same time. This is great news for a variety of continuous-duty variable-speed applications that require consistent speeds even under varying loads, such as conveyors, blowers, agitators/mixers, and pumps. |
|
Application Examples for 750 W (1 HP) Brushless DC Motor
|
Chain Conveyors |
Mixers (with hollow shaft gearhead) |
Pumps (with parallel shaft gearhead) |
Grinders (with parallel shaft gearhead) |
 |
 |
 |
 |
Motor Efficiency Comparison
The 750 W (1 HP) Brushless DC Motor achieves the highest efficiency rating in its class and earns an IE5 ultra-premium efficiency rating when paired with a BLS Series driver. The 750 W (1 HP) Brushless DC Motor can also achieve an IE5 rating when used with a 3rd party inverter/VFD. However, since we're not able to test every inverter/VFD, efficiency data for specific pairings can be requested for confirmation.
With higher efficiency, we can use less material to generate the same amount of power. The high efficiency comes with many benefits. This means that a brushless DC motor can be designed to be smaller and lighter than an equivalent AC induction motor. The higher efficiency also reduces power consumption for the brushless DC motor. Since we don't need to cool the brushless DC motor with a built-in fan, as is typically required for AC induction motors, the length of a brushless DC motor can be significantly shorter.

|
What does this mean for you? In comparison, a 750 W brushless DC motor can save up to 560 kWh of electricity consumption, $89 in electricity costs, and 260 kg of CO2 emissions when compared to a 750 W AC induction motor. In this table, we indicate the reduction of annual electricity consumption, annual electricity cost, and annual CO2 emissions when used under the following conditions. Use these values as references. |
 |
Size & Weight Comparison
|
|
In terms of size and weight, there is no competition between brushless DC motors and AC induction motors. Brushless DC motors use permanent magnets in their rotor; therefore, power losses are minimized, and the resulting higher power efficiency and lower operating temperature allow motor designs to be more compact. Since AC induction motors do not use permanent magnets, they have to induce current onto the aluminum bars on their rotors. Therefore, to overcome the efficiency losses, they need more windings and space to create the same power. With lower power efficiency, the AC induction motor also generates more heat, so it needs more surface area to cool off by conduction. When comparing motors of the same wattage/horsepower, the brushless DC motor will always be smaller and lighter. |
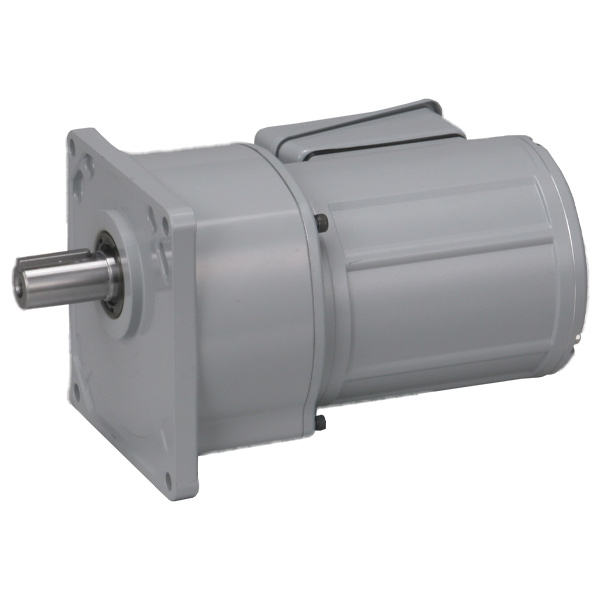
Here's a direct comparison between our 750 W (1 HP) Brushless DC Motor and a 750 W (1 HP) AC induction motor with a flange mount parallel shaft gearhead.
| 750 W Brushless DC Motor (with Parallel Shaft Gearhead) |
750 W AC Induction Motor (with Parallel Shaft Gearhead) |
 |
 |
|
Model: BL2M6750CHP-50S Frame Size: 110 mm (4.33") Motor Length: 216 mm (8.5") Weight: 6.8 kg (15 lbs) |
Model: G3K32S50-WB08TAVEN Frame Size: 198.12 mm (7.8") Motor Length: 334 mm (13.15") Weight: 22.5 kg (49.6 lbs) |
Here are the dimensional drawings. I tried to make the scales a little more accurate for both drawings for comparison.
750 W (1 HP) Brushless DC Motor with 50:1 Parallel Shaft Gearhead
Model: BL2M6750CHP-50S
Unit = mm

750 W (1 HP) 3-Phase AC Induction Motor with 50:1 Parallel Shaft Gearhead
Model: G3K32S50-WB08TAVEN / G3K32N***-WD08T◇◇EN
Unit = mm


The motor length (minus the output shaft length) is A - output shaft length = 397 mm - 63 mm = 334 mm.
Speed Torque Performance Comparison
The 750 W (1 HP) Brushless DC Motor is compatible with inverters/VFDs from other manufacturers, making it easier to upgrade your performance without having to replace the inverter/VFD. Just set the motor capacity to 750 W (1 HP), rated current to 3.6 A, and number of motor poles to 10. When driving the motor, use it at a setting frequency of 334 Hz or lower.
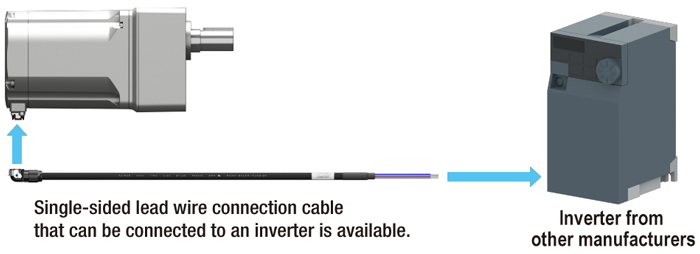
Since the same inverter/VFD can be used to drive an AC induction motor or a brushless DC motor, upgrading your motor performance can be as easy as replacing a motor.
The following torque-speed curves are for the motor only (without the gearhead). You will see that the rated torque is maintained by the brushless DC motor out to a higher RPM than the AC induction motor. Also, a brushless DC motor offers a higher max RPM than an AC induction motor (with a VFD).
750 W AC Induction Motor with VFD (General Reference)
 |
For the 1 HP AC induction motor driven with a VFD, please see the blue line. The motor generates a starting torque (~90% of rated torque) from 150 RPM, then generates 100% of its rated torque at about 300 RPM. The AC induction motor maintains 100% rated torque as it increases speed, then the torque gradually decreases from 1,800 RPM until 3,600 RPM (top speed). |
750 W (1 HP) Brushless DC Motor with Fuji FRENIC-Mini FRN0.75C2S-2J VFD
 |
For the 750 W (1 HP) Brushless DC Motor, the starting torque will depend on the VFD used. Please check the performance data and parameter settings listed for your VFD for reference. For a Fuji Electric FRENIC-Mini C2 VFD, the starting torque is about 2 Nm. The motor maintains 100% of its rated torque until 3,000 RPM, then the torque gradually decreases until 4,000 RPM (top speed). |
| Head-to-Head Results: |
|
When comparing a 1 HP brushless DC motor and a 1 HP AC induction motor with flange mount parallel shaft gearheads, there's a significant reduction in frame size (-88.12 mm), motor length (-118 mm), and weight (-15.7 kg). When comparing performance specifications, a brushless DC motor can maintain its rated torque out to a higher RPM and offers a higher peak speed than an AC induction motor driven with a VFD. |
Summary
For machine designers who do not need closed-loop speed regulation, extra space, or higher efficiency, using an AC induction motor with a VFD may be sufficient. However, for machine designers looking to upgrade their performance or make their machines more compact, brushless DC motors are the ideal choice. With compatibility with various popular VFDs, the 750 W (1 HP) Brushless DC Motor makes it easy to upgrade your motor performance without having to replace your VFD.

Our 750 W (1 HP) Brushless DC Motor is available in a round shaft, parallel shaft gearhead, or hollow shaft gearhead types with gear ratios from 5:1 to 50:1. Performance data, such as speed-torque curves, are available with popular VFD brands: ABB, Fuji, Mitsubishi, Rockwell, Siemens, Lenze, Toshiba, and Inovance. The motor is also fanless (less noise) and is rated for IP66.
Related Articles:
Case Study: Using Agricultural Automation to Improve Production Efficiency
VFD vs BLDC: Which Technology is Better for Speed Control?
Advancing Conveyor Design and Performance with Brushless DC Motors