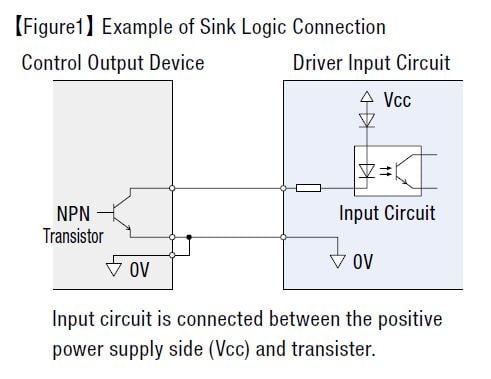
For someone who has never had experience wiring I/O for motion control, it can be scary the first time. If devices are not wired correctly, it can cause a range of issues from a motor simply not doing what's expected to irreversible product damage. I still get that nervous feeling before I press the START button on a demo. Murphy's Law, anyone?
Welcome to Oriental Motor's "Engineering Notes" Blog:
Products and technology are only valuable when coupled with skilled people and services to support them. Since 1978, ORIENTAL MOTOR U.S.A. CORP. has been building a service and support system to better serve customers. It is our goal to provide the best product and service from the design phase, through the sale and beyond.
Our blog will feature:
- Introduction to new products and technologies
- Motion control basics and application examples
- Tips for motor selection, programming, and troubleshooting
Control Basics: The Difference Between Sink and Source Logic
Topics: AC Motors, Stepper Motors, Alphastep Hybrid Control, Linear Actuators, Speed Control, BLDC Motors, Servo Motors, Motion Control Basics
A gripper is typically an end effector that is installed at the end of a robotic arm or on a cartesian robot and can be used to grip parts in order to transfer them from one location to another. However, there's more to it than just closing the jaws to pinch a part.
Topics: Stepper Motors, Robotics, Absolute Positioning, Alphastep Hybrid Control, Linear Actuators, VIDEOS, Application Examples
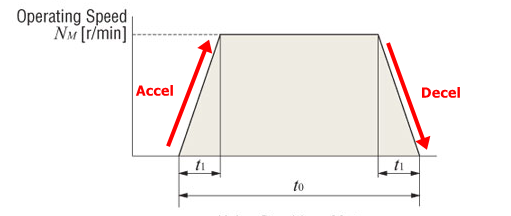
Motor Sizing Basics Part 3: How to Calculate Speed, Acceleration Torque, and RMS Torque
Now that we understand the calculations behind load torque and load inertia, we're a little closer to motor selection. You might be wondering why I separated load torque and acceleration torque calculations. That's because in order to calculate for acceleration torque, load inertia and speed must be calculated first.
Topics: AC Motors, Stepper Motors, Alphastep Hybrid Control, Linear Actuators, Speed Control, Motor Sizing, BLDC Motors, Servo Motors, Motion Control Basics
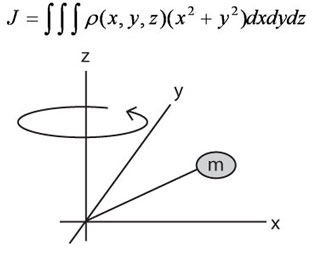
Motor Sizing Basics Part 2: How to Calculate Load Inertia
Topics: AC Motors, Stepper Motors, Alphastep Hybrid Control, Linear Actuators, Speed Control, Motor Sizing, BLDC Motors, Gearheads, Servo Motors, Rotary Actuators/Index Tables, Motion Control Basics
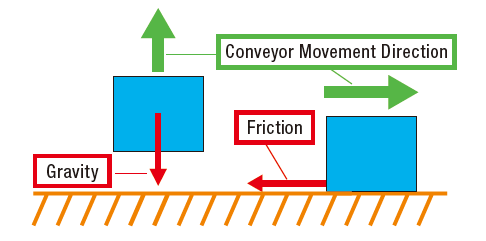
Motor Sizing Basics Part 1: How to Calculate Load Torque
Proper sizing of a motor requires that 3 criteria must be met: torque, load inertia, and speed. For the first part of this Motor Sizing Basics series, I will be explaining what load torque is, how to calculate it for specific application examples, and how it fits into the torque requirement for the application.
Topics: AC Motors, Stepper Motors, Alphastep Hybrid Control, Linear Actuators, Speed Control, Motor Sizing, BLDC Motors, Servo Motors, Rotary Actuators/Index Tables, Motion Control Basics, Conveyors
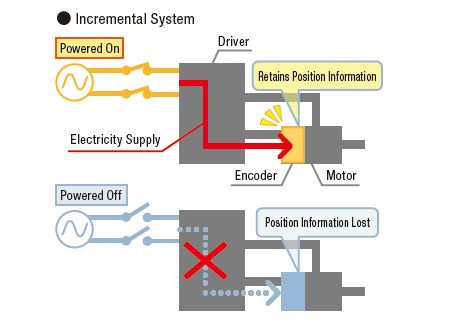
The terms "absolute" and "incremental" come up frequently in the world of position control. The exact meaning can be the type of motion done by the motor in programming terms or the type of feedback device used with the motor. In this article, we will focus on the differences between an incremental closed-loop feedback system and an absolute closed-loop feedback system.
Topics: Stepper Motors, Absolute Positioning, Alphastep Hybrid Control, Linear Actuators, VIDEOS
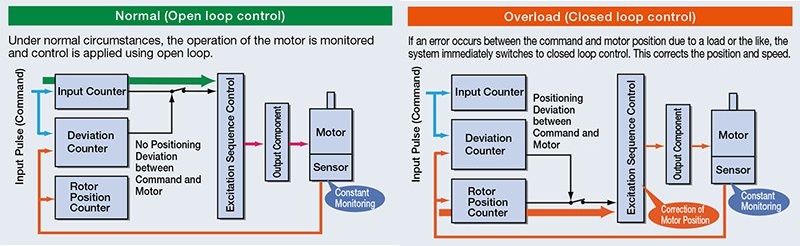
The word, "AlphaStep", describes Oriental Motor's patented Hybrid Control technology, which offers improved stepper motor performance by sensing the rotor position and automatically switching between open-loop and closed-loop operation when necessary. This post explains the unique technologies offered within the AlphaStep family of products and summarizes the numerous integrated options available. It also can serve as a website navigation guide (video added).
Topics: Stepper Motors, Absolute Positioning, Alphastep Hybrid Control, Linear Actuators, VIDEOS, Gearheads, Software, Network
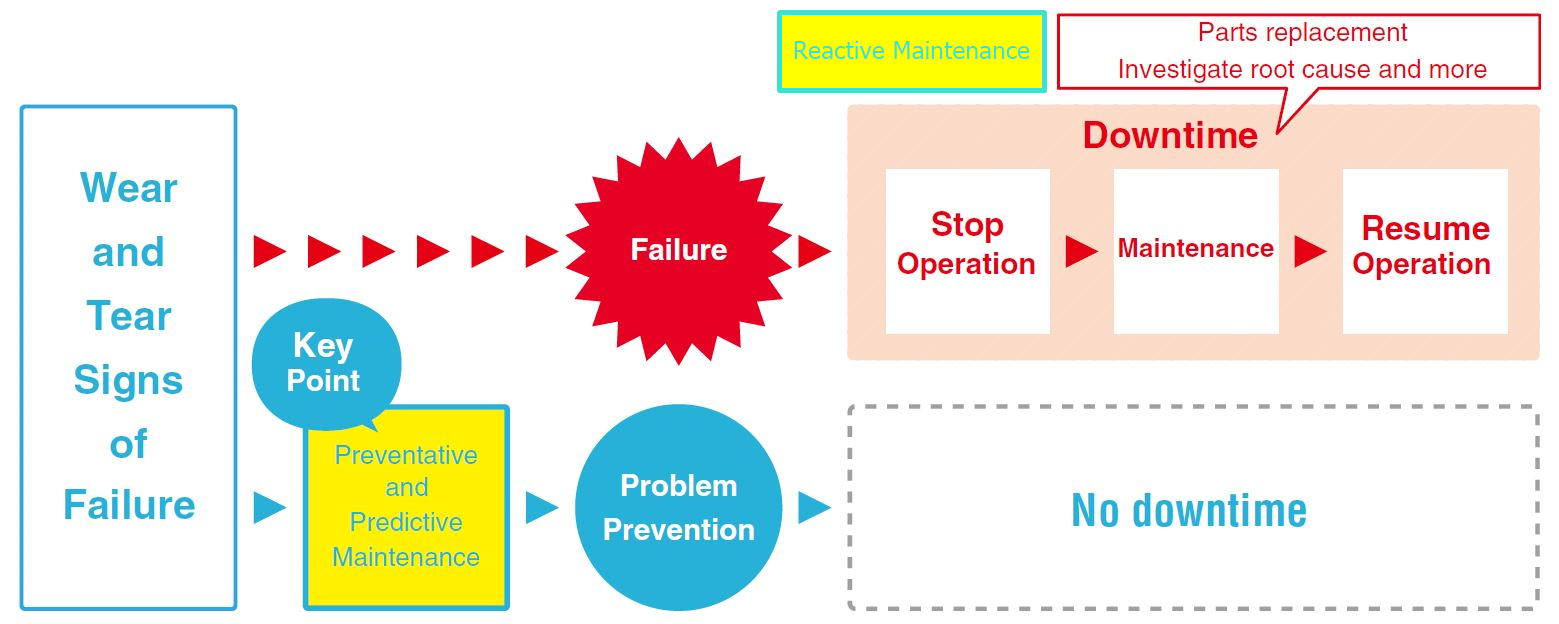
Reactive vs Preventive vs Predictive Maintenance: Why Predictive Maintenance is Better
Along with the advancement of industrial technology, maintenance methods of motion control components of a machine, such as motors, drives, and sensors, have also evolved.
Most of us still use the traditional "reactive" maintenancemethod in many aspects of life, such as replacing a dishwasher in your kitchen. People don't buy a dishwasher until theirs doesn't work anymore. Well, for factories that rely on consistent uptime for production, this wasn't the best strategy. Realizing the need for improvement, maintenance personnel started to estimate life and replace motion control components before they failed. This is called the "preventive" maintenancemethod, which also wasn't a perfect strategy for cost. More recently, with the advancement of IIoT (Industrial Internet of Things) technologies and real-time availability of status data, another method was made possible - the "predictive" maintenance method.
Topics: Stepper Motors, Linear Actuators, VIDEOS, Network, Application Examples
Robot adoption is increasing in many industries due to global efforts in reducing long term costs, maintaining quality, and freeing up time for humans to do "human" tasks. For example, by using a robot to clean floors or restock shelves in a supermarket, human employees can spend more time helping or selling to their customers. A company can either tap into this robotic trend by buying ready-made robots, or by making their own with less cost.
If engineering resources are limited, selecting the right components can reduce the difficulty and time for building a robot.
Topics: Stepper Motors, Robotics, Absolute Positioning, Alphastep Hybrid Control, Linear Actuators, Motor Sizing, VIDEOS, Gearheads, Software, Application Examples
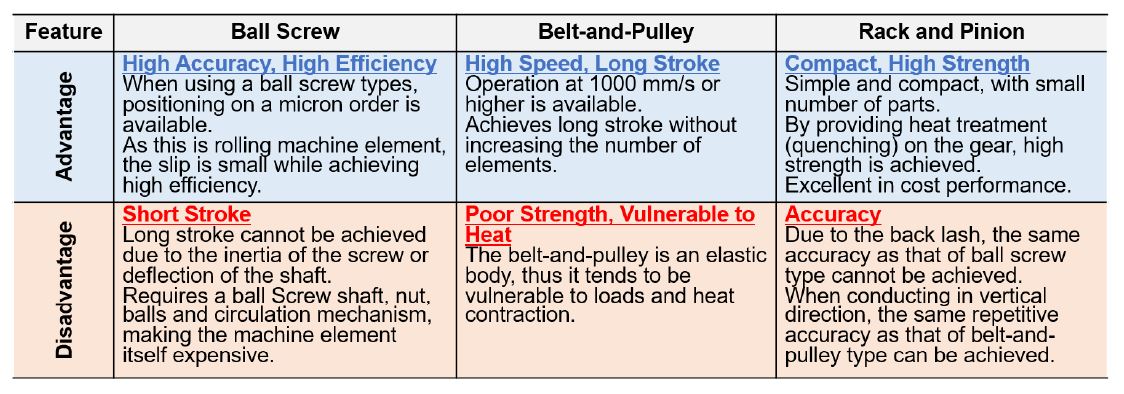
Benefits of an Absolute Rack and Pinion System Compared to Other Linear Motion Mechanisms
There are many mechanisms that convert rotary motion of an electric motor to linear motion, such as belt/chain drives, screw drives, rack & pinion drives and even CAM drives. Each mechanism offers advantages and disadvantages. Choosing the right technology can help increase load, speed, travel distance, or positioning accuracy.
Topics: Absolute Positioning, Alphastep Hybrid Control, Linear Actuators, VIDEOS, Vertical Lifts, Application Examples