In this blog post, I will explain how to easily program a timed pressing operation with our MEXE02 universal product support software. This example works for any products included in the AlphaStep AZ Series family, which also includes other series that use the same technology and software.
Welcome to Oriental Motor's "Engineering Notes" Blog:
Products and technology are only valuable when coupled with skilled people and services to support them. Since 1978, ORIENTAL MOTOR U.S.A. CORP. has been building a service and support system to better serve customers. It is our goal to provide the best product and service from the design phase, through the sale and beyond.
Our blog will feature:
- Introduction to new products and technologies
- Motion control basics and application examples
- Tips for motor selection, programming, and troubleshooting
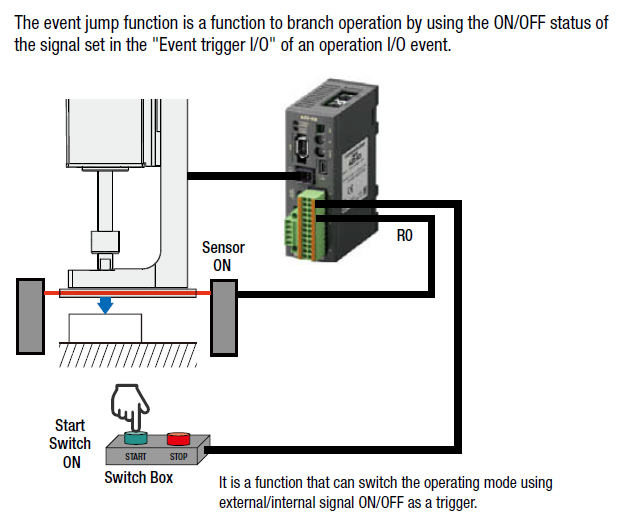
Motion Programming Example: Timed Pressing Operation
Topics: Stepper Motors, Absolute Positioning, Alphastep Hybrid Control, Linear Actuators, VIDEOS, Software, Application Examples, Motion Control Basics
There are three main types of stepper motors available in the market: PM (permanent magnet) type, VR (variable reluctance) type, and hybrid type. What are the differences, which one should you use, and how do they work?
Topics: Stepper Motors, Motion Control Basics
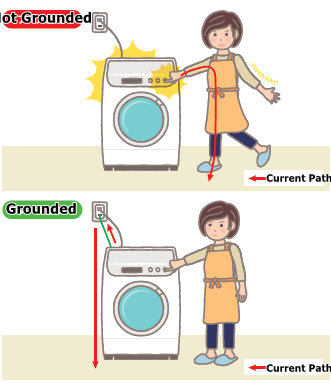
Grounding Basics: What are the Differences Between PE and FG?
Topics: AC Motors, Stepper Motors, Alphastep Hybrid Control, Linear Actuators, BLDC Motors, Servo Motors, Cooling Fans, Motion Control Basics
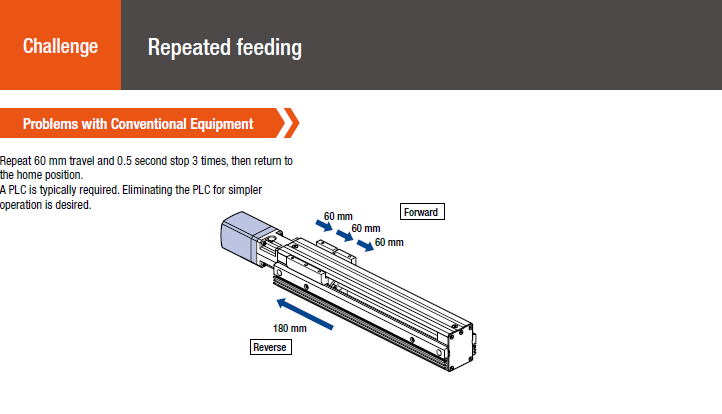
Motion Programming Example: Loop Function For Repeated Motion
No matter how many functions a product offers, without an intuitive, easy-to-use software, those functions can be difficult to implement.
Topics: Stepper Motors, Absolute Positioning, Alphastep Hybrid Control, Linear Actuators, VIDEOS, Software, Application Examples, Motion Control Basics
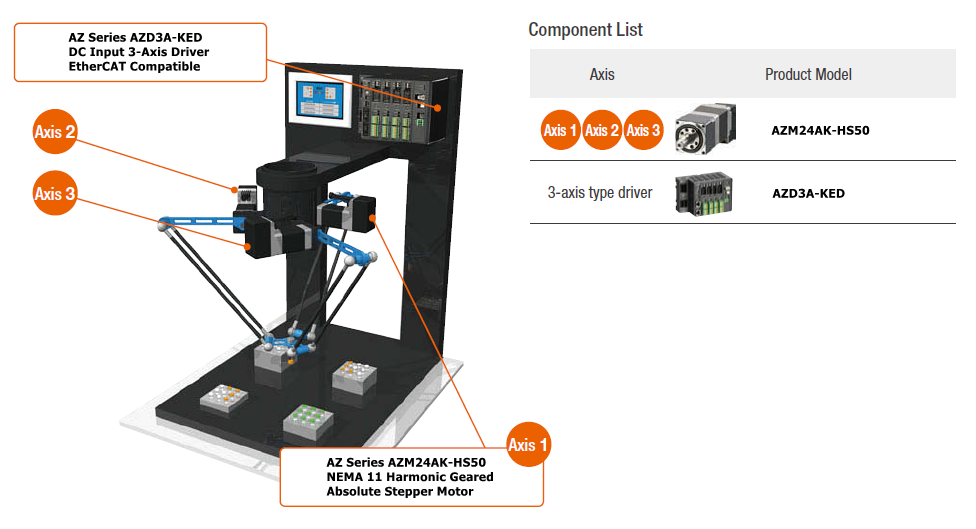
3-Axis Parallel Robot with AlphaStep Absolute Stepper Motors
Remember the days when we used to go to in-person events, such as trade shows? Robot demos have always generated a lot of foot traffic in booths. What's better to illustrate the synchronism of closed-loop stepper motors than 3 motors working together to create one specific motion?
Topics: Stepper Motors, Robotics, Absolute Positioning, Alphastep Hybrid Control, VIDEOS, Gearheads, Network, Application Examples
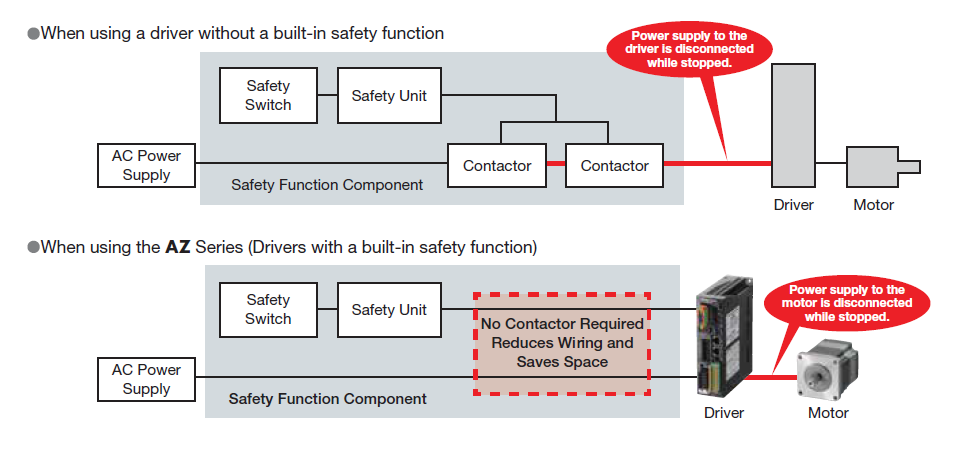
STO, or "Safe Torque Off", is a dedicated, built-in safety circuit function that makes safety easier to manage for motion devices, such as an industrial robot. It is part of the overall safety system designed to prevent injuries or damage.
Topics: Stepper Motors, Absolute Positioning, Alphastep Hybrid Control, Linear Actuators
Knowing how to use a product properly can make a huge difference in its performance and life. For example, knowing how to maintain cast iron pans properly can make them last longer. With electric motors, understanding the factors that affect motor life is the first step to extending life and decreasing costs in the long run.
Topics: AC Motors, Stepper Motors, Linear Actuators, Speed Control, Servo Motors, Service Life
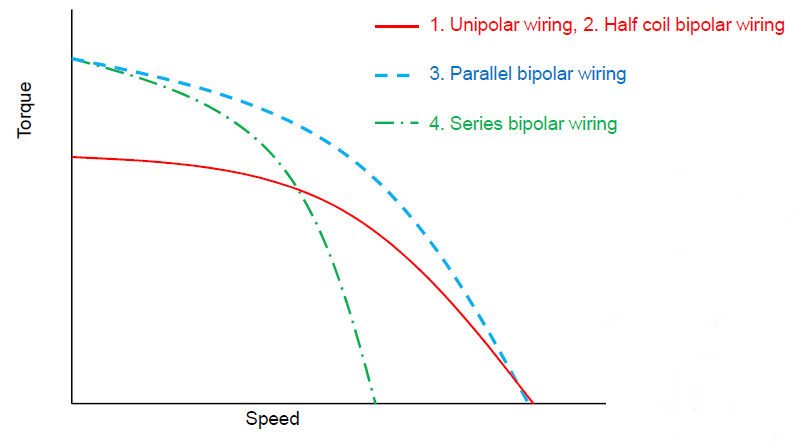
An easy way to alter the speed and torque characteristics of a stepper motor is to connect it to a different type of driver or change its wiring configuration. However, there's more to it. Knowing the pros and cons between "unipolar" and "bipolar" can make or break your stepper motor performance.
Topics: Stepper Motors, Motion Control Basics
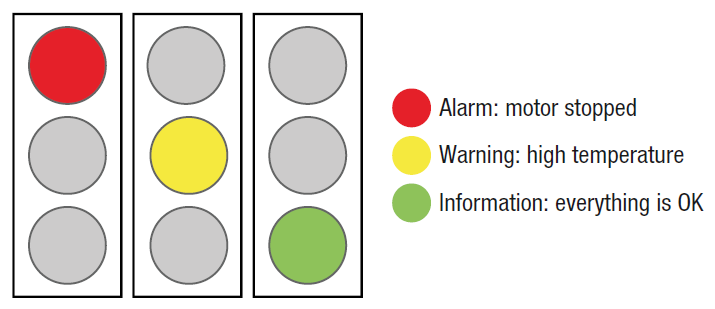
For automated factories, motor failures mean lost production and lost revenue. Being able to identify the specific issue in advance and its location is critical to maintaining production efficiency. To be successful, extra sensors must be added to detect abnormalities. There may be an easier way.
Topics: Stepper Motors, Alphastep Hybrid Control, Linear Actuators, VIDEOS, Network, Application Examples, Troubleshooting
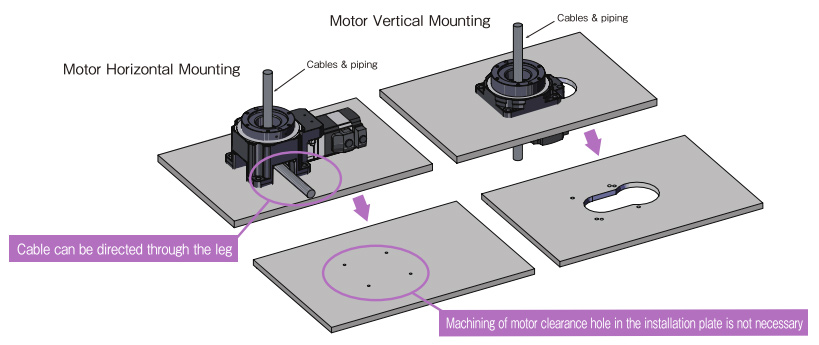
Flexible Configurations For Hollow Rotary Actuators
Topics: Stepper Motors, Robotics, Absolute Positioning, Alphastep Hybrid Control, Linear Actuators, Gearheads, Rotary Actuators/Index Tables